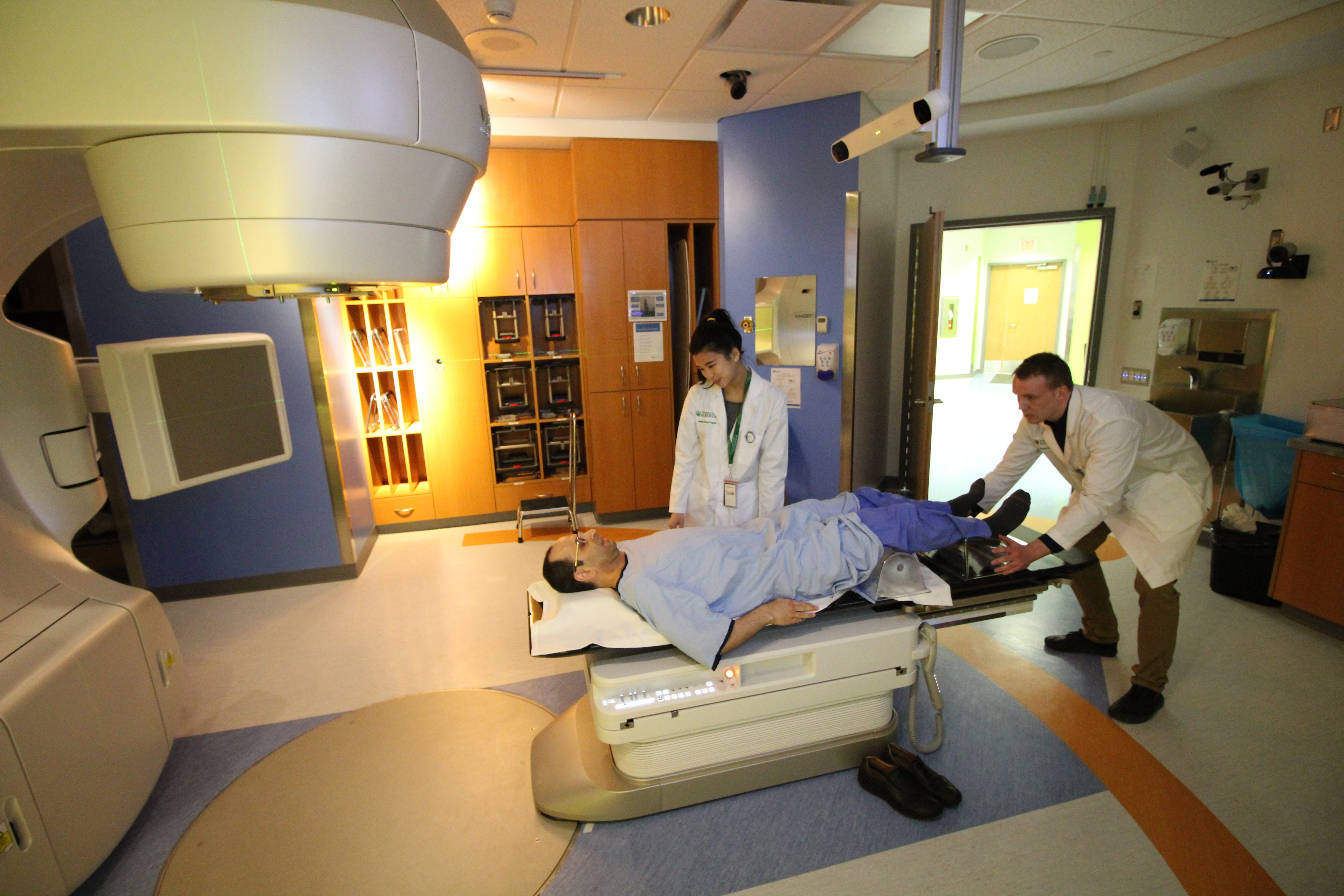
What is Radiation Therapy?
Watch a mock radiation therapy treatment session here. Click and drag on the video to change the view
What is a Radiation Therapy?
Surgery, chemotherapy and radiation therapy are the three main modalities used either alone or in conjunction with each other in the treatment of cancer.
Radiation therapy uses ionizing radiation to injure or destroy cells in the target area by damaging the DNA.
There are two main ways to deliver radiation therapy: externally or internally.
- External beam radiation therapy (EBRT) uses highly sophisticated technology to direct the radiation to a focused area of tissue.
- Internal radiation, also called Brachytherapy (BT), uses radioactive sources that are placed directly into a body cavity or the tissue of a tumour.
Who is a Radiation Therapist?
Treatment Planning & Delivery
A radiation therapist is a key team member in the treatment of cancer patients. The therapist is responsible for planning and delivering therapeutic doses of ionizing radiation as prescribed by a radiation oncologist.
The radiation therapist plays a critical role in radiation treatment planning, treatment delivery and verification, patient care and support, and delivering safe and accurate treatment. In order to perform these tasks, radiation therapists have expertise in an array of technical skills such as:
- Planning radiation treatments with sophisticated software.
- Constructing custom patient treatment devices and aids.
- Calculating radiation doses.
- Administering radiation treatments as prescribed and verifying accuracy with a variety of imaging methods.
Patient Well-Being
Radiation therapists are also responsible for managing the patient's well-being throughout the treatment period and providing education and support as needed.
Daily contact with patients requires radiation therapists to excel in behaviours and skills aimed at:
- Assessing and monitoring patients' physical and emotional needs.
- Educating patients in the care of radiation-induced side-effects and dietary requirements.
- Demonstrating excellent communication skills to interact effectively with patients, their families and other healthcare professionals.
- Using empathy and compassion to develop therapeutic relationships and rapport with patients.
- Developing an evidence-based and reflective practice.