Qiumin Tan

Qiumin Tan
Ph.D., Washington State University
Associate Professor
Office: 6-24A Medical Sciences BuildingLaboratory: 6-24 and 6-32B Medical Sciences Building
Telephone: 780-492-1523
qiumin@ualberta.ca
Awards
- Canada Research Chair Tier II in Molecular Genetics of Human Disease
Research Interests
Our research questions are:
How is early postnatal neurogenesis regulated?
What controls the migration of progenitors and newborn neurons?
What factors promote precise projection of newly generated neurons?
Most neurons in our brains arise during embryonic development and around birth. However, the mammalian brain retains the capacity to generate new neurons even throughout adulthood.
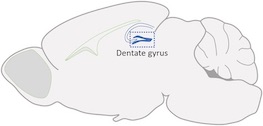
The dentate gyrus of the hippocampus is a brain region where new neurons are continuously produced. The adult-born neurons from this region are thought to be important for learning, memory formation and mood regulation.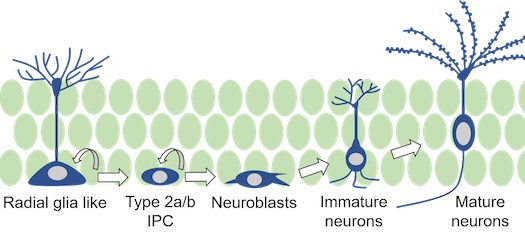
We are particularly interested in neuronal maturation during adult hippocampal neurogenesis, specifically, the stages of neuroblast and immature neuron maturation.
These are some of the questions that we are studying:
What regulates the initiation and termination of neuronal migration?
How is the dendritic architecture of new-born granule neurons built?
What confers vulnerability to cell death?
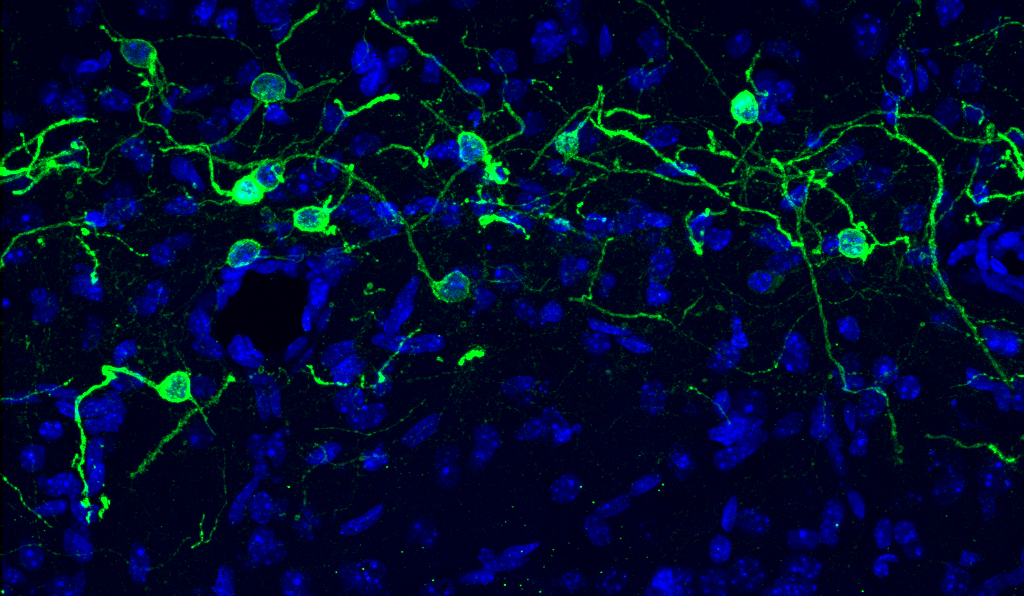
What regulates the developmental cell death of Cajal-Retzius cells?
What are the roles of Cajal-Retzius cells in the adult hippocampus?
How may Cajal-Retzius cells play a role in epilepsy?
Selected Publications
R. van Bruggen, Z.H. Patel, M. Wang, T.R. Suk, M.W.C. Rousseaux, Q. Tan (2023) A Versatile Strategy for Genetic Manipulation of Cajal-Retzius Cells in the Adult Mouse Hippocampus. eNeuro.
S. Sharma, B. Hourigan, Z. Patel, J.A. Rosenfeld, K.M. Chan, M.F. Wangler, J.S. Yi, A. Lehman, the CAUSES Study, G. Horvath, P.A. Cloos, Q. Tan. Novel CIC variants identified in individuals with neurodevelopmental phenotypes. Human Mutation, (2022) 1-11.
H. Hong, J. Lee, G.Y. Park, S. Kim, J. Park, J.S. Park, Y. Song, S. Lee, T.J. Kim, Y.J. Lee, T.Y. Roh, S.K. Kwok, S.M. Kim, Q. Tan, Y. Lee, Postnatal regulation of B-1a cell development and survival by the CIC-PER2-BHLHE41 axis, Cell Reports, 38 (2022) 110386.
B. Hourigan, S.D. Balay, G. Yee, S. Sharma, Q. Tan, Capicua regulates the development of adult-born neurons in the hippocampus, Scientific Reports, 11 (2021) 11725. https://www.nature.com/
C.S. Kao, R. van Bruggen, J.R. Kim, X.X.L. Chen, C. Chan, J. Lee, W.I. Cho, M. Zhao, C. Arndt, K. Maksimovic, M. Khan, Q. Tan, M.D. Wilson, J. Park, Selective neuronal degeneration in MATR3 S85C knock-in mouse model of early-stage ALS, Nat Commun, 11 (2020) 5304.
A. Didonna, E. Canto Puig, Q. Ma, A. Matsunaga, B. Ho, S.J. Caillier, H. Shams, N. Lee, S.L. Hauser, Q. Tan, S.S. Zamvil, J.R. Oksenberg, Ataxin-1 regulates B cell function and the severity of autoimmune experimental encephalomyelitis, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 117 (2020) 23742-23750.
Q. Tan†, H.Y. Zoghbi†, Mouse models as a tool for discovering new neurological diseases, Neurobiol Learn Mem, 165 (2019) 106902. (†co-corresponding authors)
V.V. Bondar, C.J. Adamski, T.S. Onur, Q. Tan, L. Wang, J. Diaz-Garcia, J. Park, H.T. Orr, J. Botas, H.Y. Zoghbi, PAK1 regulates ATXN1 levels providing an opportunity to modify its toxicity in Spinocerebellar ataxia type 1, Hum Mol Genet, DOI 10.1093/hmg/ddy200(2018).
M.W.C. Rousseaux, T. Tschumperlin, H.C. Lu, E.P. Lackey, V.V. Bondar, Y.W. Wan, Q. Tan, C.J. Adamski, J. Friedrich, K. Twaroski, W. Chen, J. Tolar, C. Henzler, A. Sharma, A. Bajic, T. Lin, L. Duvick, Z. Liu, R.V. Sillitoe, H.Y. Zoghbi, H.T. Orr, ATXN1-CIC Complex Is the Primary Driver of Cerebellar Pathology in Spinocerebellar Ataxia Type 1 through a Gain-of-Function Mechanism, Neuron, 97 (2018) 1235-1243 e1235.
Q. Tan†, L. Brunetti, M.W.C. Rousseaux, H.C. Lu, Y.W. Wan, J.P. Revelli, Z. Liu, M.A. Goodell, H.Y. Zoghbi†, Loss of Capicua alters early T cell development and predisposes mice to T cell lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 115 (2018) E1511-E1519. (†co-corresponding authors)
H.C. Lu*, Q. Tan*, M.W. Rousseaux, W. Wang, J.Y. Kim, R. Richman, Y.W. Wan, S.Y. Yeh, J.M. Patel, X. Liu, T. Lin, Y. Lee, J.D. Fryer, J. Han, M. Chahrour, R.H. Finnell, Y. Lei, M.E. Zurita-Jimenez, P. Ahimaz, K. Anyane-Yeboa, L. Van Maldergem, D. Lehalle, N. Jean-Marcais, A.L. Mosca-Boidron, J. Thevenon, M.A. Cousin, D.E. Bro, B.C. Lanpher, E.W. Klee, N. Alexander, M.N. Bainbridge, H.T. Orr, R.V. Sillitoe, M.C. Ljungberg, Z. Liu, C.P. Schaaf, H.Y. Zoghbi, Disruption of the ATXN1-CIC complex causes a spectrum of neurobehavioral phenotypes in mice and humans, Nat Genet, 49 (2017) 527-536. (*co-first authors)
Q. Tan, H.K. Yalamanchili, J. Park, A. De Maio, H.C. Lu, Y.W. Wan, J.J. White, V.V. Bondar, L.S. Sayegh, X. Liu, Y. Gao, R.V. Sillitoe, H.T. Orr, Z. Liu, H.Y. Zoghbi, Extensive cryptic splicing upon loss of RBM17 and TDP43 in neurodegeneration models, Hum Mol Genet, 25 (2016) 5083-5093. (Journal issue cover image.)
J. Park, I. Al-Ramahi, Q. Tan, N. Mollema, J.R. Diaz-Garcia, T. Gallego-Flores, H.C. Lu, S. Lagalwar, L. Duvick, H. Kang, Y. Lee, P. Jafar-Nejad, L.S. Sayegh, R. Richman, X. Liu, Y. Gao, C.A. Shaw, J.S.C. Arthur, H.T. Orr, T.F. Westbrook, J. Botas, H.Y. Zoghbi, RAS-MAPK-MSK1 pathway modulates ataxin 1 protein levels and toxicity in SCA1, Nature, 498 (2013) 325-331.
Laboratory Members
Graduate Students
Zain Patel
Technician
Rebekah van Bruggen
Mi Wang