Biomechanics
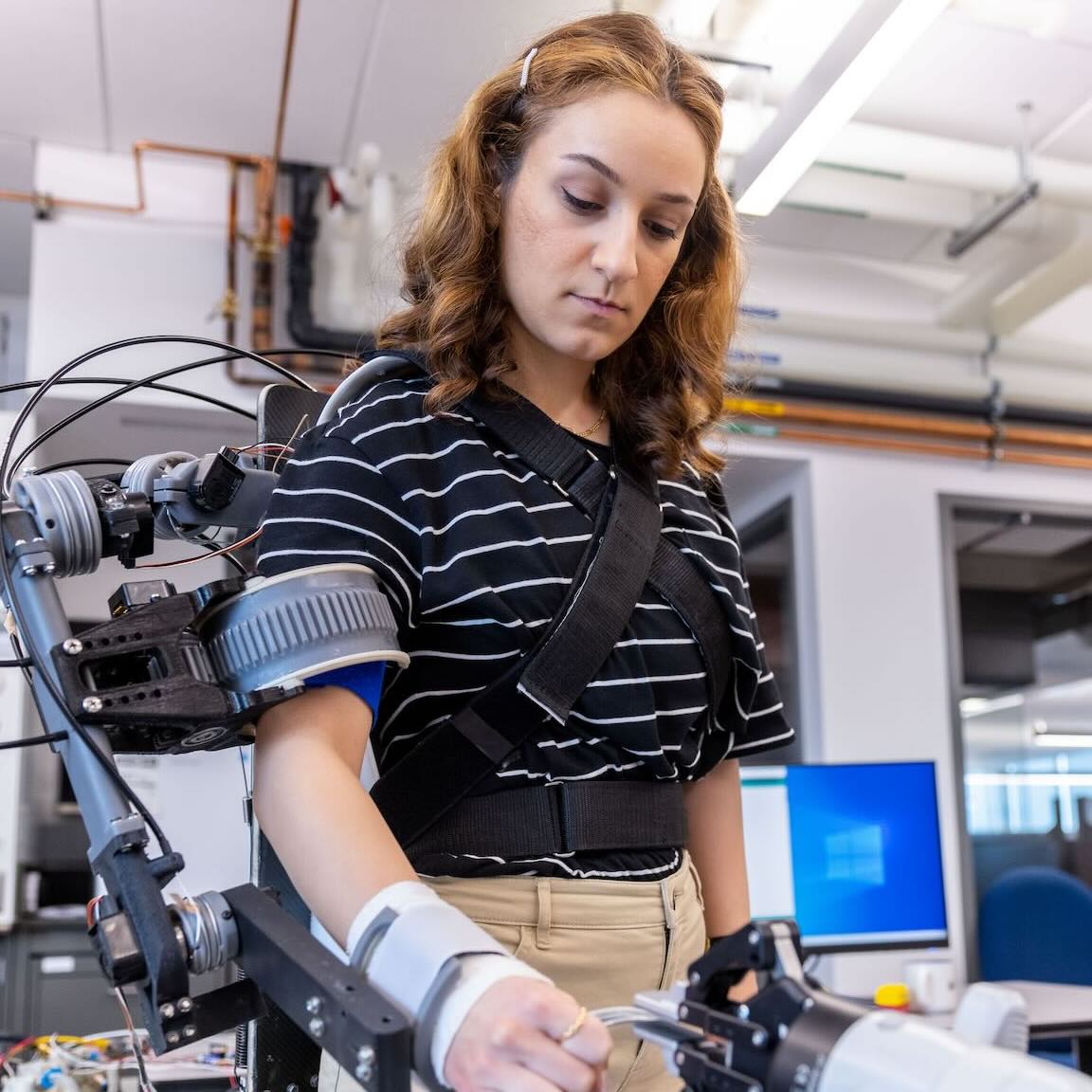
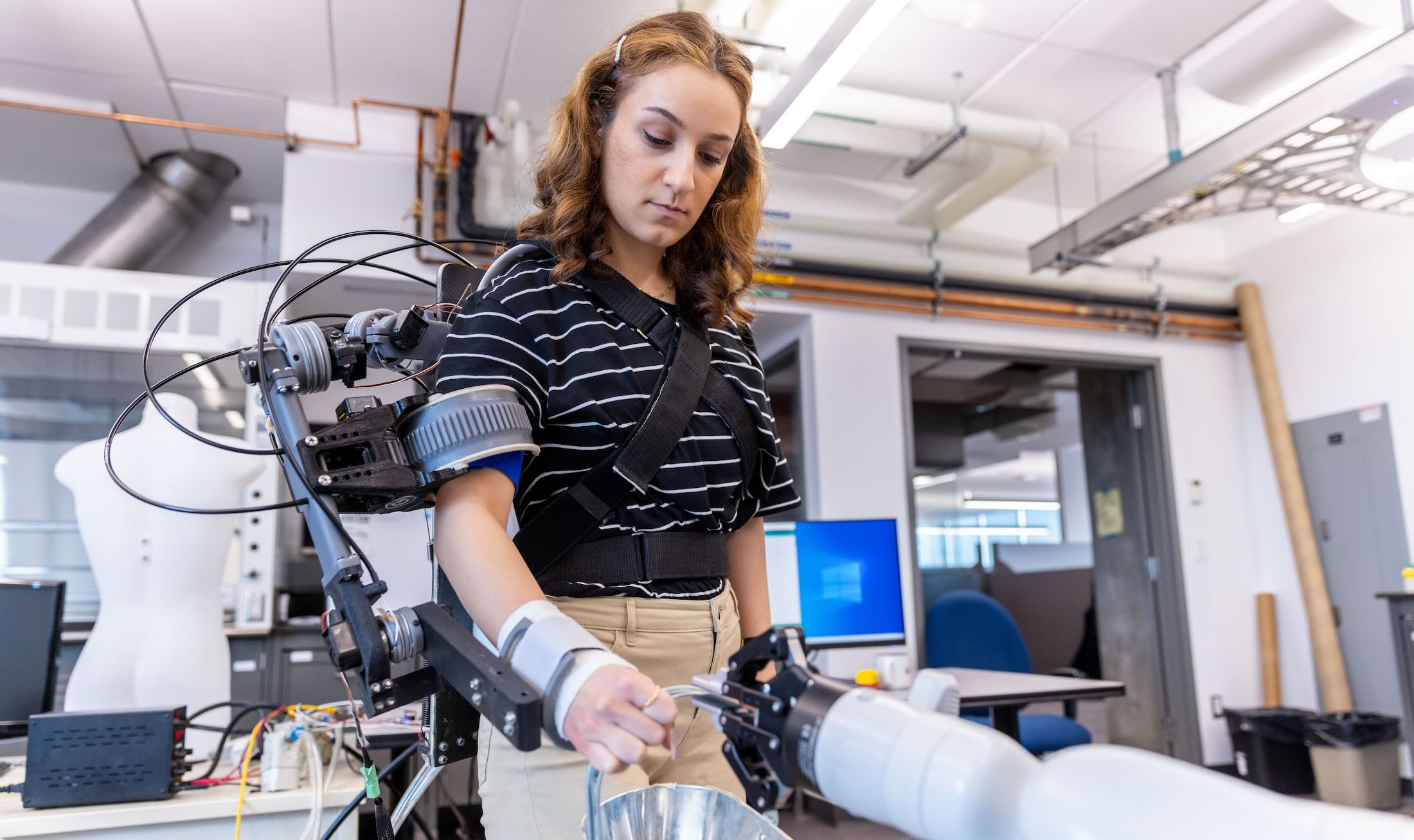

This area emphasizes the application of mechanical principles—from design and solid mechanics to fluid mechanics, mechanical control, and thermal sciences—in solving clinical and biological challenges.
Biomechanics and mechanobiology analyze the mechanics of biological processes from cells to tissues, to larger systems like musculoskeletal and cardiovascular systems, to human movement control. We leverage interactions among mechanical and civil engineers, basic biomedical scientists and clinicians from diverse specialties including orthopedics, physiotherapy, sports medicine and orthodontists to advance health and medicine.
Careers
- Forensic engineering consulting
- Medical device design and commercialization
- Rehabilitation Engineer
- Sports Biomechanist
- Ergonomist/Human Factors Engineer
- Gait Analysis Specialist
- Occupational Biomechanist
- Tissue Engineer
Area of Specialization
Cellular-level biomechanics
Cellular biomechanics addresses the interactions of physical forces with cells of different origin, including bone, cartilage, meniscus, cardiac, vasculature and muscle, as well as cancer. The questions studied are relevant to cell mechano-responsiveness (how cells sense mechanical forces), mechano-transduction (how mechanical signals are translated to biological signals) and mechano-adaptation (how cells change under the influence of mechanical forces). Novel methods of precise force application and methods for cell monitoring are developed.
- Single cell studies
- Simulated microgravity
- High speed live cell imaging
Tissue biomechanics
Tissue biomechanics is the study of the mechanical properties and behaviors of biological tissues under various forces and conditions. It involves understanding how tissues like skin, muscles, tendons, bone, and organs respond to stresses and strains. This field combines principles from biology, mechanics, and materials science to analyze and predict how tissues function and interact in both health and disease. Applications can range from designing medical implants and prosthetics to improving rehabilitation techniques and understanding injury mechanisms.
Biomechanics of human movements
Human movement biomechanics is the study of the mechanical principles and processes underlying human motion. It involves analyzing how forces and torques affect the body’s structures, including bones, muscles, and joints, to understand how movements are produced and controlled. This field combines principles from mechanics, anatomy, and physiology to assess and optimize performance, prevent injuries, and improve rehabilitation strategies. It encompasses a wide range of activities, from everyday movements like walking and lifting to complex athletic performances.