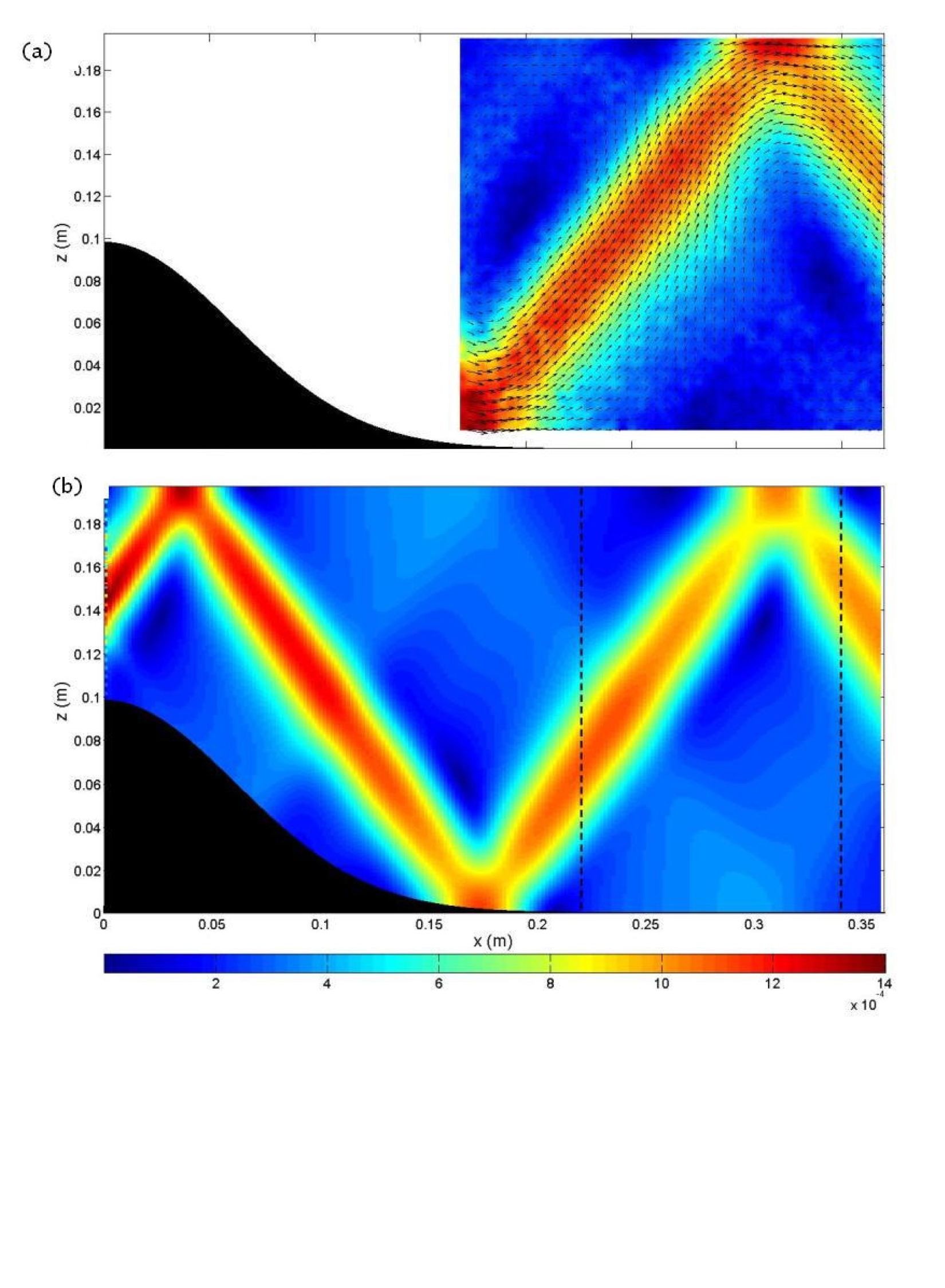
The generation of internal gravity waves from an
idealized two-dimensional Gaussian ridge. (a) Experiment (PIV); (b) theory (as
determined by modifying the theory of Petrelis et al. J. Phys. Oceanogr.
36, 2006). [Figure adapted from Echeverri et al., J. Fluid Mech., 636, 2009]